Introduction:
In today's rapidly evolving digital landscape, where businesses and individuals are more interconnected than ever, the importance of cybersecurity cannot be overstated. As technology advances, so do the threats and vulnerabilities that can compromise sensitive information and disrupt critical operations. Based on the illustration by Cyber Security Agency of Singapore, the overview of cyber threats in Singapore has been on the rise, with 48% of system disruptions for businesses and 60% of data loss for non-profit organizations in 2023. To address these challenges, organisations must embrace proactive measures, and one such essential practice is the cybersecurity audit.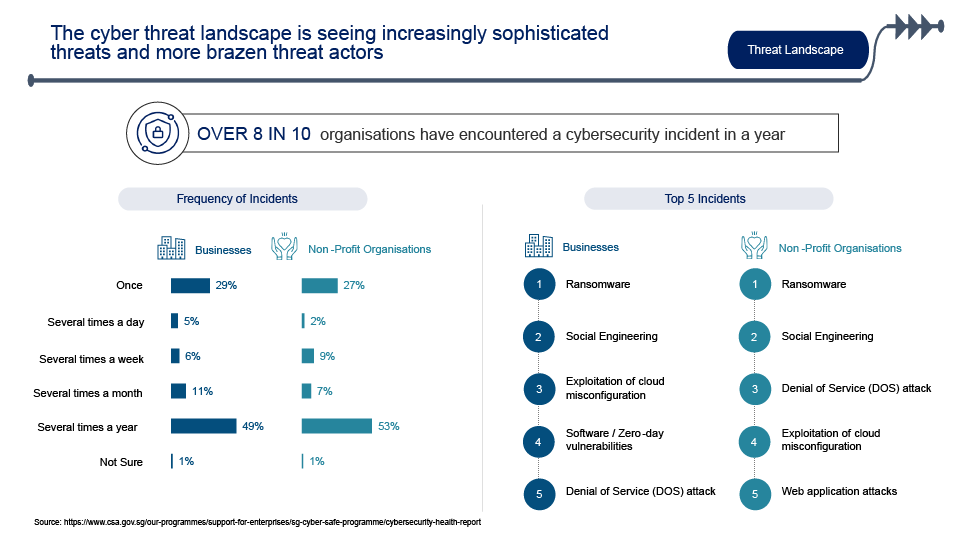
Source: https://www.csa.gov.sg/our-programmes/support-for-enterprises/sg-cyber-safe-programme/cybersecurity-health-report
Understanding Cybersecurity Audits:
A cybersecurity audit involves a comprehensive examination of an organisation's information systems, policies, and procedures to assess the effectiveness of its security measures. This process helps identify potential vulnerabilities, evaluate existing safeguards, and ensure compliance with relevant regulations and industry standards.In the modern era, where data breaches and cyber-attacks have become increasingly sophisticated, a cybersecurity audit serves as a crucial tool in safeguarding sensitive information and maintaining the trust of customers, stakeholders, and partners.
Cybersecurity audits can provide an overview of a business’s security posture by identifying vulnerabilities, risks and threats that might cause an impact. Cybersecurity audits covers numerous areas, such as:
- Physical Security - Review of role-based access controls, multifactor authentication, etc.
- Network Security - Review of network security, monitoring capabilities of network security, anti-virus configuration, etc.
- Operational Security - Review of security policies, controls, procedures, etc.
- Data Security - Review of encryption used, data security at rest and in transit, network access control, etc.
- System Security - Review of hardening processes, privileged account control management, patching processes, etc.
Apart from these areas, cybersecurity audits also cover other aspects such as Cybersecurity Awareness Training, third-party management, Business Continuity Plan (BCP), cybersecurity risk and governance, cybersecurity risk management, and incident response. While these additional areas may not be applicable to all businesses, it is essential for business owners to recognise the benefits of understanding how cybersecurity audits can enhance the maturity of their cybersecurity practices to mitigate cybersecurity risks effectively.
How often should Cybersecurity Audits be conducted?
There is no definitive answer to determine the frequency of cybersecurity audits to be conducted in an organisation. Several factors can contribute to conducting a cybersecurity audit, including the nature of the organisation's business, the severity of the risks involved, compliance with legal or regulatory requirements, and the size of the organisation.The frequency of cybersecurity audits can be based on certain criteria:
Major Changes: Whenever an organisation's IT infrastructure undergoes significant changes, a cybersecurity audit should be considered. This ensures that the changes are adequately protected with the appropriate security measures in place. Major changes may include the implementation of new technologies, network expansions, and significant upgrades.
Annual Audits: Conducting annual cybersecurity audits provides organisations with valuable insights into their security posture. These audits help identify necessary changes, as well as existing and new risks and vulnerabilities. By performing annual cybersecurity audits, organisations can stay informed about the latest developments in cybersecurity trends.
Regulatory Requirements: Some organisations are mandated to comply with cybersecurity regulations based on the nature of their business. To ensure compliance with the latest regulations, a cybersecurity audit can ensure that all regulatory requirements are met to avoid legal complications. Examples of regulatory standards include SOC 2 (System and Organisational Compliance), the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and the Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS).
Incident Response: A thorough cybersecurity audit must be conducted by any organisation that has experienced an incident or security breach. This is a requirement as part of the incident response process. Through a cybersecurity audit, the affected organisation can identify the root cause of the security breach, conduct an impact assessment, and strengthen security measures to manage or prevent similar security incidents in the future.
Key Impact Areas of Cybersecurity Audits:
Based on the figure, there are a few key impact areas of cybersecurity audits which can help organisations create a secure security environment. It is important to note that these impact areas can be adjusted to meet the specific organisational business needs for better identification of cybersecurity concerns.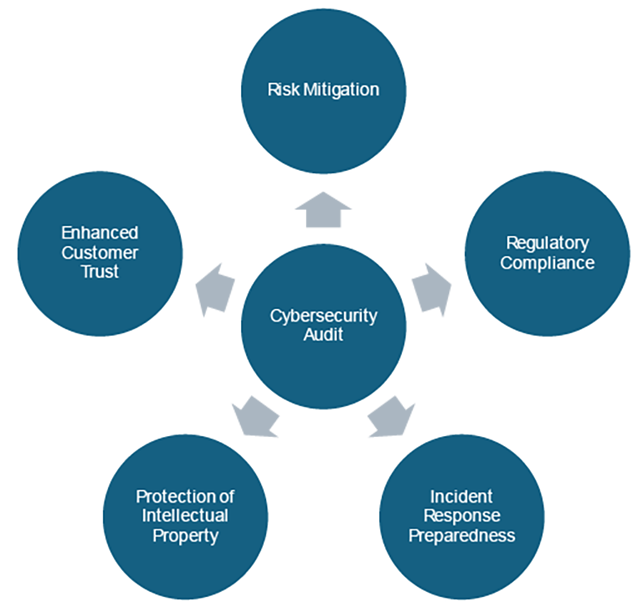
Figure 1: Key Impact Areas of Cybersecurity Audits
Regulatory Compliance: In today's world, various industries are subject to strict regulations and compliance requirements concerning the protection of sensitive data. Cybersecurity audits ensure that organisations adhere to these regulations, such as the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act (HIPAA), and others. Non-compliance can result in severe legal consequences, fines, and damage to an organisation's reputation.
Incident Response Preparedness: Cybersecurity audits help organisations assess their incident response capabilities. By simulating potential cyber-attacks or reviewing historical incidents, organisations can refine and enhance their response plans. This proactive approach ensures that, in the event of a security breach, the organisation can effectively contain the threat, minimize damage, and recover swiftly.
Protection of Intellectual Property: Businesses today heavily rely on intellectual property, proprietary information, and trade secrets. Cybersecurity audits aid in protecting these valuable assets by evaluating the effectiveness of access controls, encryption methods, and other security measures. This safeguards an organisation's innovation and competitive edge.
Enhanced Customer Trust: With data breaches making headlines regularly, consumers are increasingly concerned about the security of their personal information. Undertaking cybersecurity audits and publicly demonstrating a commitment to robust security practices can significantly enhance customer trust. A reputation for strong cybersecurity measures can become a competitive advantage, attracting, and retaining customers who prioritise data protection.
Conclusion:
In today's interconnected world, where cyber threats are ever-present, cybersecurity audits are not just a recommended practice but a necessity. The impact of these audits extends beyond the organisation itself, influencing customer trust, regulatory compliance, and overall resilience in the face of evolving cyber threats. As businesses continue to digitalise their operations, embracing and prioritising cybersecurity audits will be key to maintaining a secure and resilient digital environment.
References:
Chinnasamy, V. (29 May, 2023). Indusface. Retrieved from Indusface: https://www.indusface.com/blog/what-is-cyber-security-audit-and-how-it-is-helpful-for-your-business/
Sergeja Slapnicar, T. V. (2021). Effectiveness of Cybersecurity Audit. 21. Retrieved from Researchgate: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/357861875_Effectiveness_of_cybersecurity_audit
Sharma, S. (6, 2022). Singapore’s cybersecurity outlook: Cyberattacks, threats, laws & more. Retrieved from ETCIO: https://ciosea.economictimes.indiatimes.com/news/internet/singapores-cybersecurity-outlook-cyberattacks-threats-laws-more/92223424
Sweny, G. (1 7, 2023). Agile Blue. Retrieved from Agile Blue: https://agileblue.com/what-is-a-cybersecurity-audit-why-is-it-important/
Tim Maurer, A. N. (2021). International Monetary Fund. Retrieved from International Monetary Fund: https://www.imf.org/external/pubs/ft/fandd/2021/03/global-cyber-threat-to-financial-systems-maurer.htm
Cyber Security Agency - Cybersecurity Health Report: https://www.csa.gov.sg/our-programmes/support-for-enterprises/sg-cyber-safe-programme/cybersecurity-health-report